High blood sugar can cause a number of health problems. Most notably, it can trigger the onset of diabetes, especially in people with a family history of the disease. People with diabetes must monitor their diet to prevent their blood sugar from running dangerously high or too low, but even those without diabetes should keep their blood sugar within normal limits. With some adjustments to your diet and your lifestyle, you can keep blood sugar normal, possibly reducing the risk of needing medication in the future.
Method 1 : Creating a Diet That Will Lower Your Blood Sugar
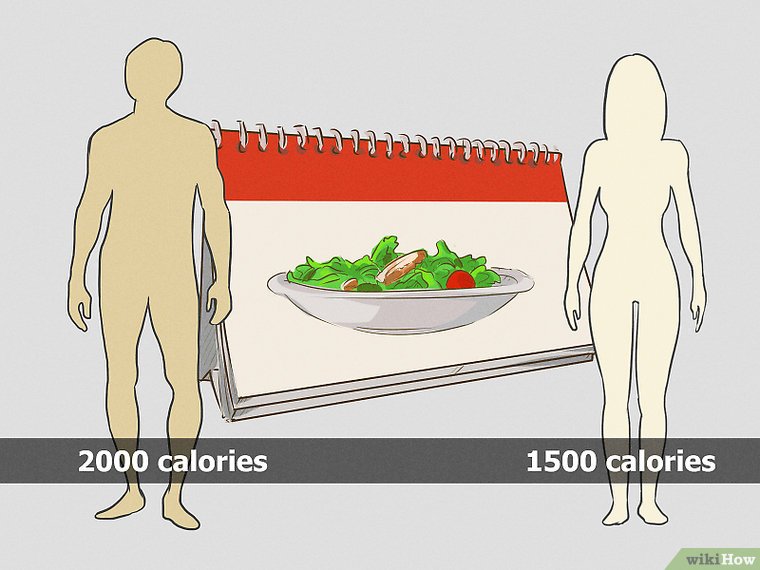
1. Figure out how many calories you should consume per day.Determining the right number of calories will help you eat the right amount of food. Eating excess food can in turn lead to excessive sugar entering your bloodstream. How many calories you should eat depends on your body size and whether you want to maintain your weight. In general, you should:
- Consume 1,200 to 1,600 per day if you are a small woman, a medium-sized woman who wants to lose weight, or a medium-sized woman who does not exercise much.
- Consume 1,600 to 2,000 calories per day if you are a large woman who wants to lose weight, a small man, a medium-sized man who does not exercise much or wants to lose weight, or a large man who wants to lose weight.
- Consume 2,000 to 2,400 calories per day if you are a medium to large man who exercises a lot, a large man at a healthy weight, or a medium to large woman who exercises a lot.

2. Check the glycemic index (GI) of food you eat often. The glycemic index is a system that ranks carbohydrates based on how much they raise blood sugar levels after consumption. Knowing how foods will affect your blood sugar can help you plan out your meals and make better food choices.
- Foods with a low GI rating are less likely to raise your blood sugar than those with a high rating.
- Be aware that the glycemic index may not catch all sources of sugar beyond glucose. Other sugars, such as fructose and lactose, add to your blood sugar as well.
- Keep in mind that the glycemic index is based on eating foods on their own, which is not how most people eat. If you consume a simple sugar, make sure to pair it with a source of protein or fat to slow its absorption.
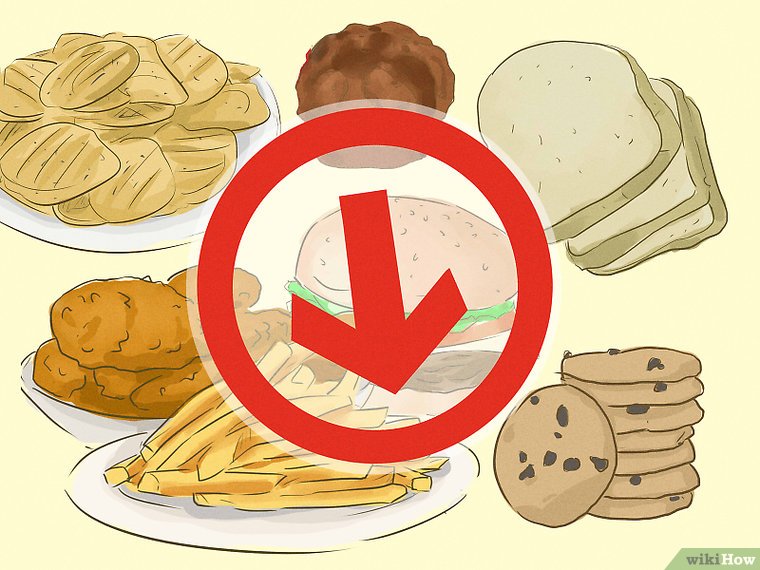
3. Limit your refined carbohydrates. In particular, reduce the amount of refined carbohydrates you’re consuming, such as white flour baked products, sugary cereals, and fried foods. On most days you should not be eating any refined carbohydrates if you are trying to lower your blood sugar.
- Carbohydrates have a greater impact on your blood sugar levels than anything else because they break down into glucose very quickly.

4. Make a meal plan and stick to it. Once you know how much you should be eating and what you should and shouldn’t be eating, make a specific plan for all your meals. If you can stick to your plan, you will have a diet that lowers your blood sugar.
- It can be hard to stick to a new diet. Talk to your friends and family about needing their support. You can also discuss your diet with your doctor and see if they have any suggestions about how to get support to keep on your diet.
Method 2 : Picking Foods That Promote Low Blood Sugar

1.Choose healthy carbohydrates. Ultimately all foods are converted into blood sugar and consumed to make energy. However, it’s important to avoid foods where this happens very quickly. Sugars and starches (as found in white bread, potatoes, and many other carbohydrates) are converted most rapidly and should be avoided. On the other hand, whole grains and legumes (lentils and beans) are converted more gradually and are better sources of energy for almost everyone.
- You should eat some carbohydrate at each meal, but only a small portion.
- Healthy whole grains include barley, oats, spelt, wheat, kamut and brown rice.
- Breads and cereals are healthy provided you pick multi grain or whole grain varieties and steer clear of the high fat and high sugar varieties. Also, choose bread and cereals containing less than 140mg of sodium per serving..
- Make sure that you are counting your carbs if you have diabetes. You should aim for 45 to 60 grams per meal and 15 to 30 grams per snack.

2. Add more fiber to your diet. Fiber cleanses your system and soluble fiber helps control your blood sugar levels. Most vegetables are high in fiber, especially those with leafy greens. Many fruits, nuts, and legumes are also rich in fiber, as are whole-wheat products.
- Soluble fiber is very important for maintaining good health. It is found in such foods as beans, nuts, oat bran, and seeds.
- Flax-seeds are both a good source of fiber and for maintaining balanced blood sugar. Grind two tablespoons with 10 ounces of water and consume each morning to gain its benefits.
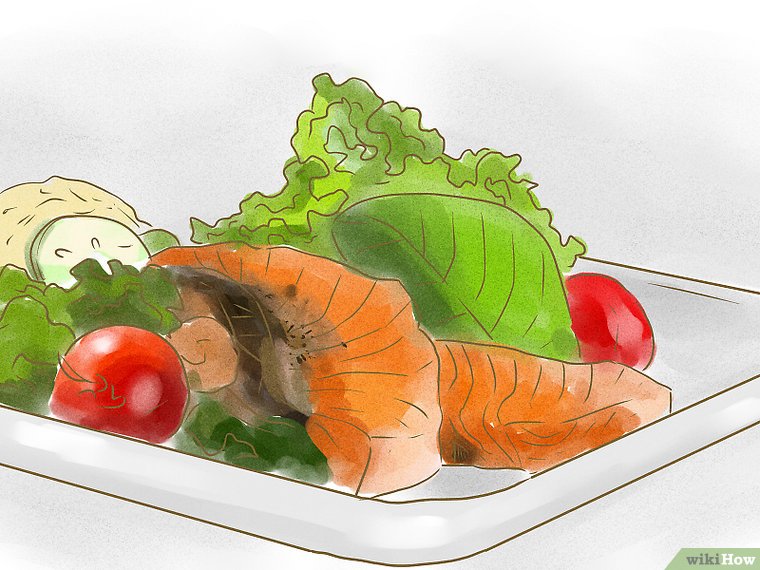
3. Eat fish twice a week or more. Fish is high in protein, which is good to eat for maintaining your blood sugar. Fish also has less fat and cholesterol than meat and poultry. Many types of fish, including salmon, mackerel, and herring, also have high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, which lower fats called triglycerides and promotes overall heart health. Avoid fish prone to high levels of mercury, however, like swordfish and king mackerel.
- Proteins are good for you and can sometimes help moderate the rise in sugar.
- Other sources of healthy, lean protein include legumes, nuts, seeds, peas, turkey, and chicken. You might also consider protein drinks with 15g or less of sugar.

4. Eat more oatmeal, beans, and lentils. Unsweetened oatmeal digests slowly, which prevents your blood sugar from spiking up dramatically while providing your body with the slow-release energy it needs. Lentils and legumes (beans) are just as good. All of these foods contain soluble fiber, which delays sugar and carbohydrate absorption, which is good.
- Some people feel that these foods give them indigestion and gas until their systems get accustomed to them, so use your judgement.

5. Look for non-starchy vegetables. Broccoli, spinach, and green beans are excellent examples of non-starchy vegetables that you should eat a lot of. These vegetables are low in carbohydrates, so they do not affect your blood sugar very much, but they are also high in fiber and other nutrients.
- Starchy vegetables to avoid include potatoes, corn, and peas.

6. Look for non-starchy vegetables. Broccoli, spinach, and green beans are excellent examples of non-starchy vegetables that you should eat a lot of. These vegetables are low in carbohydrates, so they do not affect your blood sugar very much, but they are also high in fiber and other nutrients.
- Starchy vegetables to avoid include potatoes, corn, and peas.

7. Drink more water instead of sugary beverages. Soda and sugary juice drinks raise your blood sugar quickly. Substituting these drinks with water, sugar-free tonic water and sparkling water can quickly reduce your sugar intake.
- Many commercially available waters are also flavored, which may make them more appetizing than plain water. However, make sure that these beverages do not contain any added sugar.
- You can add strawberries, lemon or lime slices or a dash of orange juice to flavor sparkling water at home without adding empty calories.
- Try to drink 6-8 glasses of fluids a day that consist mainly of water to ensure that you’re adequately hydrated.

8. Sprinkle cinnamon onto your food. Some experts believe that cinnamon has a moderate effect at reducing blood sugar levels, especially in people with diabetes. The results are far from conclusive, but early studies do support the claim.
- Do not rely on cinnamon as a magic solution to high blood sugar! It should be treated as an extra addition to all the other solutions.
Method 3 : Preventing High Blood Sugar

1. See a doctor to talk about blood sugar. If you are concerned about keeping your blood sugar under control, it’s important to talk to your doctor about it. Your doctor will understand your specific health conditions and so will be able to help you personalize a program that is right for you.
- In some cases, your doctor may refer you to specialists who can help you maintain your blood sugar. For example, they may send you to see a registered dietitian who can help you design a diet that will help lower your blood sugar.

2. Take your medication regularly, if necessary. If you have developed diabetes, then you likely need to control your blood sugar with medication, such as insulin. If you have been prescribed medication, take it on a regular basis as prescribed.
- In addition to taking your medication, you will need to test your blood sugar on a regular basis. This allows you to understand what level your blood sugar is at and if you need to adjust it with medication.
3. Maintain a healthy weight.There are a variety of things you can do to lower your blood sugar in addition to using diet. One of the key things to focus on is keeping at a healthy weight. Even if you are overweight, lowering their weight can improve their chances of avoiding diabetes.
- Talk to your doctor about what kind of weight management program might be right for you, given your specific medical conditions.

4. Exercise regularly. Exercising as often as possible will help keep your blood sugar under control because it will help maintain your blood glucose levels and help keep you at a healthy weight. Try to exercise 3 to 5 times a week for between 30 and 60 minutes at a time.
- You can do a wide variety of exercises to help with your blood sugar, including aerobic exercise, strength training, balance and flexibility work, and relaxation focused exercise, such as yoga.
- If you have diabetes, make sure to bring a snack any time you exercise and check your blood sugar before you work out. You will need to eat it if your blood sugar drops.
- Talk to your doctor about what exercise programs might be right for you. They can advise you about what to do given your specific health conditions.
